Carotid artery stenosis, or Carotid Stenosis in medical terms,
is a condition commonly found in the elderly and those with risk factors for vascular disease.
This condition results from the accumulation of fat and calcium in the arterial walls, causing the blood vessels to narrow.
This leads to reduced blood flow to the brain, increasing the risk of stroke, which can result in disability or death.
Currently, there is a new treatment method called Carotid Balloon Angioplasty and Stenting,
which is a non-surgical treatment that provides good results, quick recovery, and high safety.
Screening and Diagnosis
1. Carotid Ultrasound:
- Part of annual health check-ups for at-risk groups
- Painless, no injection required
- Can measure blood flow velocity and assess stenosis level
2. MRI and MRA of neck and brain blood vessels:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) shows brain tissue
- MRA (Magnetic Resonance Angiography) shows blood vessels
- Provides detailed information on both brain structure and blood vessels
- Used for screening or confirming ultrasound results
3. Examination when stroke symptoms are present:
- If the patient shows stroke symptoms such as limb weakness or slurred speech
- CT scan of the brain is performed first to rule out cerebral hemorrhage
- Followed by MRI/MRA or CT Angiography to examine neck and brain blood vessels
Indications for Treatment
This treatment method is suitable for patients with the following characteristics:
- Carotid artery stenosis greater than 70%
- Symptoms of transient ischemic attack (TIA) or minor stroke
- Those at high risk for open surgery
- Those who have previously undergone carotid surgery and have recurrent stenosis
Carotid Stenting and Balloon Angioplasty Procedure
Treatment is performed under general anesthesia. The treating physician will insert a catheter through the femoral artery in the groin.
Angiogram with X-ray:
Contrast medium is injected into the main artery. A Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) X-ray machine is used to image the blood vessels. The resulting image shows the location and severity of the stenosis.
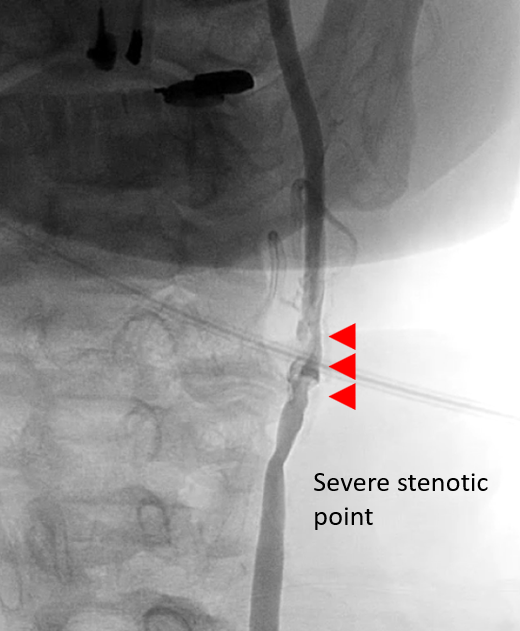
Showing carotid artery stenosis in the neck before treatment from cerebral angiography under DSA
3D Calculation Program:
Special software creates 3D images from the angiogram, analyzing the length, diameter, and shape of the stenosed vessel, and accurately calculating the stenosis level. This helps in selecting the most appropriate stent size and length.
Insertion of Protective Embolic Device:
A special device is inserted into the blood vessel above the stenosis point to catch blood clots or debris that may dislodge and block the upper brain, reducing the risk of cerebral complications during the procedure.
Balloon Angioplasty:
A catheter with a small balloon is inserted into the stenosed blood vessel. The balloon is expanded to flatten the fatty plaque against the vessel wall and increase the vessel’s diameter, improving blood flow. Pre-dilation (expansion before stent insertion) and/or post-dilation (expansion after stent insertion) may be performed depending on the nature of the stenosis.
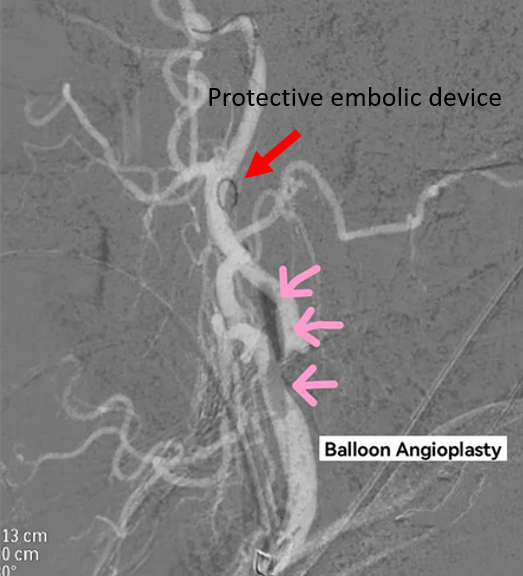
Showing the insertion of a protective embolic device during balloon angioplasty
Stent Insertion:
After expanding the blood vessel with the balloon, a stent (wire mesh tube) is inserted to prop the vessel open. The size and length of the stent are chosen based on the 3D image data, and the stent is expanded to fit snugly against the vessel wall.
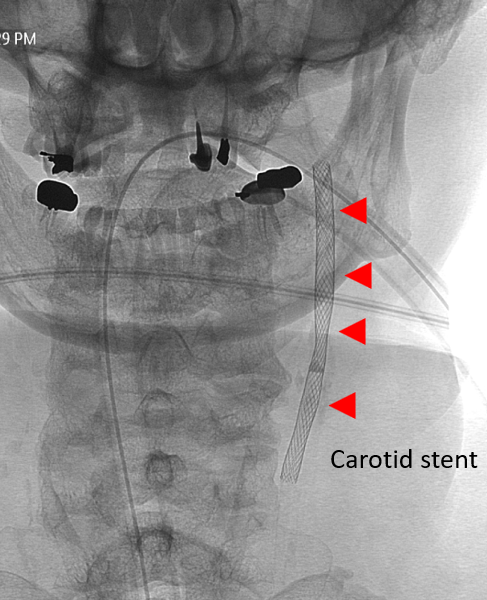
Showing the insertion of a carotid artery stent in the neck after treatment
Result Verification:
The DSA X-ray machine is used to check blood flow after stent insertion, assessing whether the blood vessel has opened sufficiently. If the result is unsatisfactory, additional post-dilation may be performed.
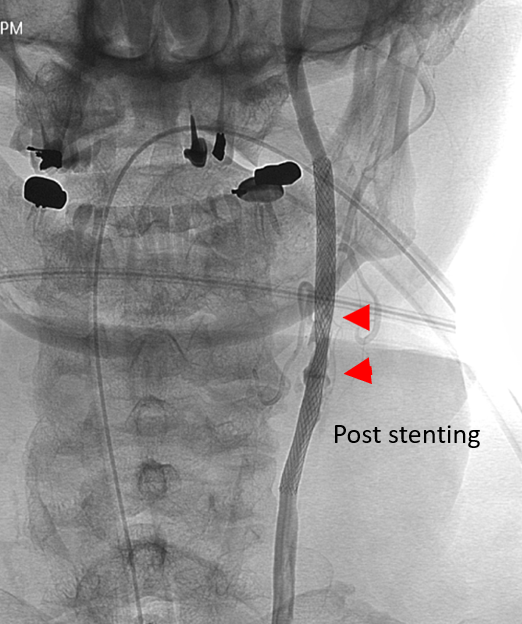
Showing improved blood flow after treatment
Advantages of the Treatment
- No open surgery: No surgical incision in the neck
- Quick recovery: Most patients can return home within 2-3 days
- Low risk: Suitable for patients at high risk for open surgery
- Good treatment outcomes: Effectively reduces the risk of stroke
- Less pain: Patients feel more comfortable than with open surgery
Treatment Outcomes
- Most patients experience immediate improvement after treatment
- Reduces the long-term risk of stroke
- Patients can return to daily activities faster than with open surgery
Post-Treatment Care
- Take antiplatelet medication as prescribed by the doctor
- Avoid strenuous exercise for 1 week
- Avoid lifting heavy objects or bending the head for prolonged periods
- Attend follow-up appointments regularly
- Control risk factors for vascular disease, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, high blood lipids
Recommendations
If you are over 50 years old, have a history of high blood pressure, diabetes, high blood lipids, or smoke, you should consult a doctor for carotid artery stenosis screening. Early detection and treatment can effectively reduce the risk of stroke.
Treatment with Carotid Balloon Angioplasty and Stenting is a safe and highly effective option. If you are diagnosed with carotid artery stenosis, don’t hesitate to consult a specialist to consider the most appropriate treatment for you.
References
- Brott TG, Howard G, Roubin GS, Meschia JF, Mackey A, Brooks W, et al. Long-Term Results of Stenting versus Endarterectomy for Carotid-Artery Stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(11):1021-31. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1505215
- Paraskevas KI, Veith FJ, Ricco JB. Carotid Artery Stenting Versus Carotid Endarterectomy for Carotid Artery Stenosis: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Short-Term and Long-Term Outcomes. Ann Vasc Surg. 2020;69:427-37. doi:10.1016/j.avsg.2020.05.070
- Sardar P, Chatterjee S, Aronow HD, Kundu A, Ramchand P, Mukherjee D, et al. Carotid Artery Stenting Versus Endarterectomy for Stroke Prevention: A Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;69(18):2266-75. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2017.02.053
*All copyright of pictures: my own photo (Dr. Ittichai Sakarunchai)

Assoc. Prof. Ittichai Sakarunchai, M.D.
Assistant Professor of Neurosurgery & Interventional Neuroradiology
BNH Neuroscience Centre