Dengue Fever
Dengue Fever is a viral infection transmitted by the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes, causing epidemics worldwide, especially in countries with hot and humid climates like Thailand.
In Thailand, dengue fever is one of the most prevalent infectious diseases, especially during the rainy season. The disease can occur in both rural and urban areas and affects all age groups, including children and adults.
Dengue fever is caused by any one of four types of dengue viruses. Should you have had dengue fever in the past, you still can be infected again by the other virus types. In addition, previous infection with dengue fever increases your risk of severe symptoms if you get dengue fever again.
list of contents
Symptoms of dengue fever
Dengue fever has a wide range of symptoms. It is a disease that can lead to severe and life-threatening conditions if not treated promptly and correctly. Symptoms can vary depending on the severity and the health status of the patient. Common symptoms include:
Initial stage:
- High fever: A sudden and very high fever.
- Headache: A feeling of heaviness and pain in the head.
- Fatigue: Feeling of fatigue and lack of energy.
- Red, painful eyes: Eyes are red and painful.
- Joint and muscle pain: Joints and muscles are painful and feel tired.
- Rash: Rashes appear on the skin, especially on the arms and legs.
Critical stage:
- Decreasing fever: After 3-7 days, the fever will drop, but other more severe symptoms may arise.
- Bleeding symptoms: There might be bleeding from the nose, mucous membranes, skin, or internal bleeding.
- Decrease in blood pressure: Rapid decrease in blood pressure, which could lead to shock.
- Gastrointestinal symptoms: Vomiting and diarrhea.
- Decreased function of vital organs: Potential issues in the functioning of vital organs such as the kidneys, heart, and liver.

Diagnosis:
- History-taking related to travel history or risk factors.
- Blood tests to detect the virus or related antibodies.
Treatment:
- There is no specific drug that can directly treat dengue fever. The treatment usually focuses on symptom relief and might include administering fluids and electrolytes intravenously.
- In severe cases, a large amount of fluids and electrolytes may be required, and additional treatments such as blood transfusion might be necessary.

Prevention:
- Vaccine: If you live in an area where there’s an outbreak or at risk of infection, getting vaccinated might be another preventive measure.
- Eradicate mosquito breeding sites: Eliminate breeding grounds for mosquitoes, such as water bottles, rainwater pipes, water tanks, or use chemicals to kill mosquito larvae.
- Prevent mosquito bites: Use mosquito repellent and wear clothing that covers the skin. Apply skin repellents or spray them on clothes. Use mosquito nets when sleeping.
- Monitor symptoms: If initial symptoms resembling dengue fever appear, such as high fever, body aches, and headaches, you should see a doctor immediately for diagnosis and treatment.

Dengue vaccine
The dengue vaccine is one method to prevent dengue fever. The dengue vaccine helps the body’s immune system to develop immunity against the dengue virus.
Who should get the vaccine?
- Those aged between 4 to 60 years at the time of the first vaccine dose.
- Individuals residing in areas with dengue fever outbreaks.
- People traveling to areas with dengue outbreaks.
- It’s recommended for those who have been previously infected with dengue to get vaccinated to prevent more severe infections in subsequent encounters.
Precautions:
- Avoid administering this vaccine to pregnant women or those breastfeeding.
- For those who have recovered from dengue, it is recommended to wait at least 6 months before receiving the dengue vaccine. After infection, the body will have immunity against the disease, which decreases over time. Vaccination during a period of high immunity might reduce the vaccine’s efficacy.
Side effects of the dengue vaccine:
The dengue vaccine is safe. The majority of side effects from the dengue vaccine are usually mild and temporary, such as pain or swelling at the injection site, slight fever, or feeling fatigued. These symptoms typically improve within one or two days.
Where to get the Dengue Fever vaccine?
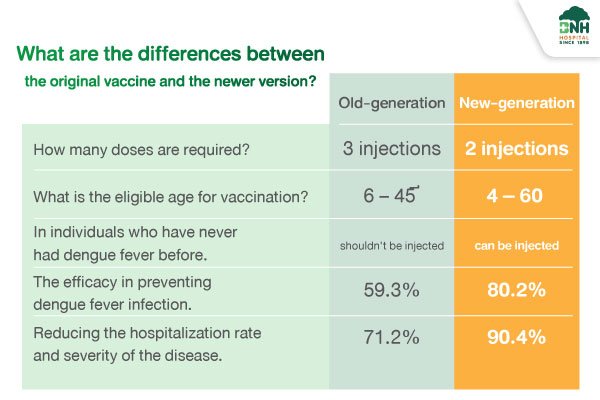
- It’s a new-generation vaccine.
- Only 2 injections required (with a 3-month gap).
- Suitable for ages 4 to 60.
- It can be administered to both individuals who have had dengue fever before and those who haven’t.
- Protection against all 4 strains of dengue fever is up to 80.2%.
- Reduces hospitalization and disease severity is up to 90.4%.
BNH Hospital wants to protect you and your loved ones from dengue fever. Get the new 4-strain dengue fever prevention vaccine package at a special price.

Dengue vaccine price:
Special dengue vaccine package price: 2 doses for only 4,400 Baht. Promotion is available today until December 31, 2023 only.
- The package includes the cost of 2 doses of the dengue fever vaccine, to be administered 3 months apart.
- The price does include hospital service charges.
- The price does not include doctor fees.
Terms of Service:
- The vaccine is suitable for those aged 4 to 60.
- The package price is for adult ages 15 and above.
- for children under 15 years old please contact the Pediatrics Department for the price of vaccine
- Doctor consultation is required before vaccination.
- Please make an appointment before get the service.
- The package includes the cost of 2 doses of the dengue fever vaccine, administered 3 months apart.
- The price includeห doctor fee and hospital service fee.
- This package cannot be exchanged, changed, or refunded in cash.
- Service is available from 07:00 AM to 08:00 PM at BNH Hospital only.
- For those aged 4 to 15, please contact the Pediatrics Department on the 2nd floor.
- For those aged 15 and older, please contact the Internal Medicine Department on the 4th floor.
- You can get the service from today until December 31, 2024
- For more details, please contact: Line @Mbarce
According to data from the Department of Disease Control, there were 156,097 cases of dengue fever in 2023. It is predicted that in 2024 there will be an increase in cases, with a possible total of 276,945 cases.